Stock Market Reactions: Understanding How Markets Respond to News and Events
Stock Market Reactions: Understanding How Markets Respond to News and Events The stock market is a dynamic and ever-changing environment where prices fluctuate based on a variety of factors. Stock market reactions refer to how investors and traders respond to news, economic data, corporate announcements, and global events. These reactions can lead to rapid price movements, volatility, and shifts in market sentiment.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- What drives stock market reactions?
- Types of market-moving events
- How investors can anticipate and respond to market shifts
- Historical examples of major market reactions

What is a Stock Market Reaction ?
A stock market reaction refers to how investors collectively respond to new information—such as company earnings, Federal Reserve announcements, inflation data, or global events—and how that response impacts stock prices. For example, strong corporate earnings might trigger a positive reaction, pushing share prices higher, while disappointing news can cause a negative reaction, leading to a sell-off. These reactions are driven by investor sentiment, supply and demand, and future expectations, making the market highly dynamic. Understanding stock market reactions helps traders and investors anticipate trends, manage risks, and make smarter financial decisions.
Go to Homepage
What Causes Stock Market Reactions?
Stock prices are influenced by supply and demand, which are driven by:
1. Economic Data Releases
Reports like GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation (CPI, PPI), and interest rate decisions can trigger immediate market movements.
Example: A higher-than-expected inflation report may lead to fears of rising interest rates, causing stocks to drop.
2. Corporate Earnings & News
Company-specific news, such as earnings reports, mergers, leadership changes, or
scandals, can cause sharp price swing
Example: If Apple reports better-than-expected earnings, its stock (and possibly the broader tech sector) may surge.
3. Geopolitical Events
Wars, elections, trade tensions, and diplomatic conflicts create uncertainty, often leading to market volatility.
Example: The 2020 COVID-19 crash was a reaction to global lock downs and economic uncertainty.
4. Central Bank Policies
Decisions by the Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), or other central banks on interest rates and monetary policy heavily impact markets.
Example: When the Fed raises rates, growth stocks often decline due to higher borrowing costs.
5. Market Sentiment & Behavioral Factors
Fear and greed drive short-term market movements. Indicators like the VIX (Volatility Index) measure investor anxiety.
Types of Stock Market Reactions
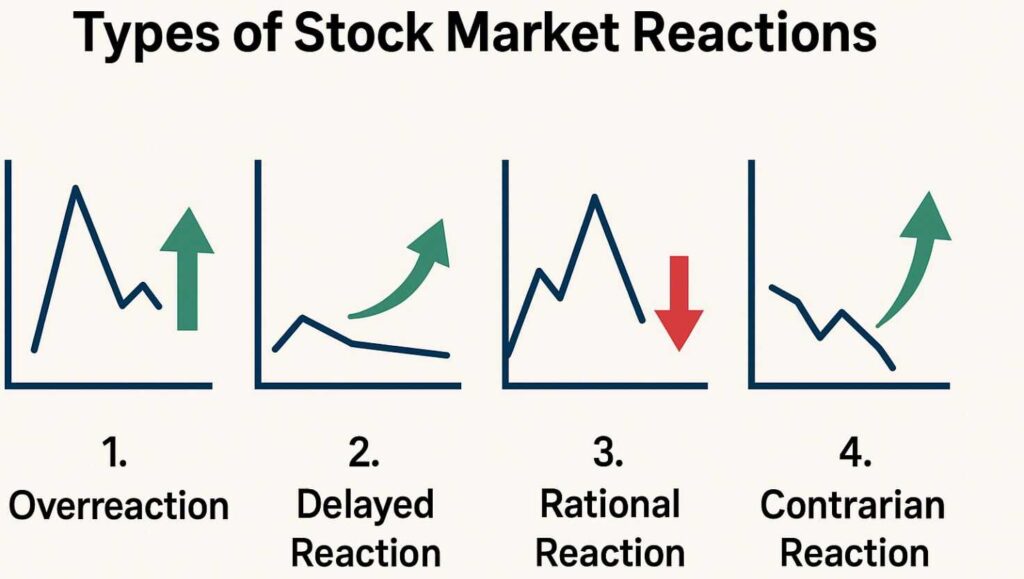
| Reaction Type | Description | Example |
| Overreaction | Markets move excessively due to panic or hype | Meme stocks like Game Stop (2021) |
| Delayed Reaction | Market takes time to digest news | Gradual sell-off after multiple rate hikes |
| Rational Reaction | Prices adjust logically based on data | Stocks rise after strong earnings reports |
| Contrarian Reaction | Market moves opposite to expectations | “Buy the rumor, sell the news” events |
How Can Investors Respond to Market Reactions?
1. Stay Informed
- Follow financial news (Bloomberg, CNBC, Reuters)
- Use economic calendars to track key events.
2. Diversify Your Portfolio
- Spread investments across sectors to reduce risk.
- Include defensive stocks (utilities, healthcare) during volatility.
3. Use Stop-Loss Orders
- Automatically sell a stock if it drops below a set price to limit losses.
4. Avoid Emotional Trading
- Stick to a long-term strategy instead of panic selling.
5. Consider Inverse ETFs & Hedging
- Tools like S&P 500 Put Options or Gold ETFs can protect against downturns.
Historical Examples of Major Market Reactions

- 2008 Financial Crisis – Lehman Brothers’ collapse triggered a global market
- 2020 COVID-19 Recovery – Markets rebounded after stimulus packages and
- 2022 Russia-Ukraine War – Oil prices surged, tech stocks fell due to supply chain fears.
Final Thoughts
Stock market reactions are inevitable, but understanding their causes can help investors make smarter decisions. By staying informed, diversifying, and avoiding emotional trading, you can navigate volatility more effectively.

Hurrah, that’s what I was exploring for, what a information! existing here at this
website, thanks admin of this web site.